|
|
Calorimetry
 Scientists measure the change in thermodynamic quantities in thermochemical equations using a device known as a calorimeter
Scientists measure the change in thermodynamic quantities in thermochemical equations using a device known as a calorimeter  . One kind of calorimeter, known as a coffee cup calorimeter, is shown at left. Coffee cup calorimeters are usually used to measure changes that take place in solution. Since the reaction taking place in the calorimeter is open to the atmosphere, the enthalpy change is measured directly by the device. The insulation provided by the styrofoam ensures that any heat absorbed or released by the system (reactants and products) goes only to the solvent in the cup. In other words, the surroundings are restricted to the solvent in the cup. The thermometer allows the DT of the surroundings to be measured. By the First Law of Thermodynamics (see the Energy module), we know any heat lost by the system must be absorbed by the surroundings, or: . One kind of calorimeter, known as a coffee cup calorimeter, is shown at left. Coffee cup calorimeters are usually used to measure changes that take place in solution. Since the reaction taking place in the calorimeter is open to the atmosphere, the enthalpy change is measured directly by the device. The insulation provided by the styrofoam ensures that any heat absorbed or released by the system (reactants and products) goes only to the solvent in the cup. In other words, the surroundings are restricted to the solvent in the cup. The thermometer allows the DT of the surroundings to be measured. By the First Law of Thermodynamics (see the Energy module), we know any heat lost by the system must be absorbed by the surroundings, or:
-qsystem = qsurroundings
Using DT, which can be measured, and the heat capacity of the solvent in the coffee cup, the heat lost by the system can be calculated. Since the pressure is constant, this is equal to the enthalpy change for the process.
 When 1.00 g of NaOH(s) is dissolved in 100.0 mL of H2O (l) in a coffee cup calorimeter, the temperature of the water rises from 25.00 to 27.66 ºC. The heat capacity of water is 4.184 J/gºC. Find DH for the dissolving process:
When 1.00 g of NaOH(s) is dissolved in 100.0 mL of H2O (l) in a coffee cup calorimeter, the temperature of the water rises from 25.00 to 27.66 ºC. The heat capacity of water is 4.184 J/gºC. Find DH for the dissolving process:
NaOH(s) 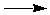 NaOH(aq) DH = ? NaOH(aq) DH = ?
Step 1: Define the system and surroundings. Write your answer in the space below, then click on the check button.
|
|