
IMAGE. 10-mL graduated cylinder.
|
Step 1: Determine the scale increment:
To find the scale increment, subtract the values of any two
adjacent labeled graduations and divide by the number of intervals
between them.
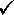 What is the scale increment for the 10-mL graduated cylinder? Answer
What is the scale increment for the 10-mL graduated cylinder? Answer
In the 10-mL graduated cylinder, first subtract
8 mL - 6 mL = 2 mL. Next, count that there are ten intervals between
the labeled graduations. Therefore, the scale increment is 2
mL/10 graduations = 0.2 mL/graduation. Step 2: Use the graduations to find all certain digits:
Use the labeled graduations and the scale increment to find
the certain digits in the measurement.
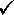 What are all of the certain digits for solution in the 10-mL graduated cylinder shown? Answer What are all of the certain digits for solution in the 10-mL graduated cylinder shown? Answer
The first digit is 6, since the last labeled graduation below the meniscus is six. Next, use the scale increment. There are three unlabeled graduations below the meniscus, and each graduation represents 0.2 mL, for an additional 0.6 mL. Therefore, the certain digits of the reading are 6.6 mL. Step 3: Estimate the uncertain digit and obtain a reading:
Estimate the distance that the meniscus lies between the two graduations as a decimal fraction and multiply by the scale increment.
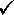 What is the volume you should record for the solution in the image above?
Answer What is the volume you should record for the solution in the image above?
Answer
The meniscus is about one tenth of the way to the next graduation, so the final digit in the reading is (0.1 increment) * (0.2 mL/increment) = 0.02 mL. The uncertain reading is added to the certain digits, so the volume measurement is 6.62 mL. |