|
|
Combustion Analysis
Another common method of analysis is combustion analysis. This method relies on the fact that many compounds will burn in the presence of oxygen gas. If the products of this reaction can
be isolated, information about the original compound can be obtained.
Compounds that contain carbon and hydrogen will react with oxygen to form carbon dioxide and water. If you worked through the General Stoichiometry Module, you may remember the equation for the combustion of methane:
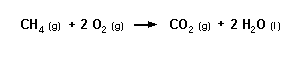
You can see in this equation that all of the carbon is converted to carbon dioxide and all of the hydrogen is converted to water. If the CO2 produced can be measured, the amount
of carbon in the original sample can be calculated. Similarly, if the H2O can be measured, the amount of hydrogen in the original sample can be calculated. A simple apparatus used to measure the amount of carbon dioxide and water that is formed is shown below.
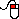 |
Click on buttons to see steps of combustion analysis. Clicking on mouse will reset.
|
 |