Example:
What volume of carbon dioxide at 37°C (body temperature) and 740 torr is produced by the metabolism of 1.0 g ethyl alcohol (C2H5OH)? The balanced equation is:
![]()
Solution
To sove this problem find the number of moles of CO2 formed. Then use the ideal gas equation to convert from the number of moles of carbon dioxide to a volume;
Wanted
Liters (V) of CO2 at 37°C and 740 torr
Given
1.0 g C2H5OH
Conversion factors
1 mol C2H5OH = 46.1 g C2H5OH
1 mol of C2H5OH yields 2 mol CO2
37°C = 310 K
Arithmetic equation
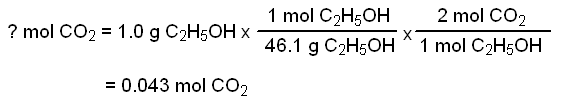
Substiuting this value into the ideal gas equation gives:
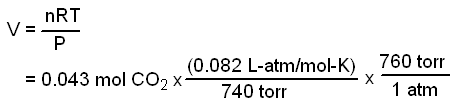
Answer
![]()