Standard Free Energy of Formation (DGfº)
Gibbs Free Energy is a state function, just as enthalpy and entropy are. This means that the DG of the sum of a series of reactions is equal to the sum of the DG's of the individual reactions:
| C(s) + |
1/2 O2 |
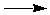 |
CO(g) |
DGº = -137.168 kJ |
| CO(g) + |
1/2 O2 |
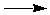 |
CO2 |
DGº = -257.191 kJ |
| ________________________________________________________________ |
| C(s) + |
O2 |
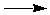 |
CO2 |
DGº = -394.359 kJ |
Similar to enthalpy, thermodynamics tables contain an entry for the standard free energy of formation (DGfº). These are the free energy changes for a very specific kind of thermochemical equation:
- one mole of a compound is formed
- the reactants are elements in their standard states
- the standard free energy of formation of an element in its standard state is zero
The standard free energies of formation can be used to calculate the free energy change of any reaction under standard conditions.
 Calculate the free energy change for the formation of methanol from carbon monoxide and hydrogen gas:
Calculate the free energy change for the formation of methanol from carbon monoxide and hydrogen gas:
|