Biomolecules:
Protein 1
Protein Sequences (Primary Structure)
Many proteins have thousands of amino acids. To save space, their sequences are usually written using the abbreviated amino acid names, like the three-letter codes used in this module.
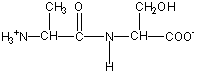 Does the order of the amino acids when written on paper make a difference in the structure? For example, is Ala-Ser the same as Ser-Ala? It turns out that they're not. For example, shown at the right is the structure of Ala-Ser. Notice how the Ala has a free amine group (the -NH3+ group) while the Ser has a free acid group (the -COO- group). By convention, protein sequences are written from the end with the free -NH3+ group (the N terminus
Does the order of the amino acids when written on paper make a difference in the structure? For example, is Ala-Ser the same as Ser-Ala? It turns out that they're not. For example, shown at the right is the structure of Ala-Ser. Notice how the Ala has a free amine group (the -NH3+ group) while the Ser has a free acid group (the -COO- group). By convention, protein sequences are written from the end with the free -NH3+ group (the N terminus
![]() ) to the end with the free -COO- group (the C terminus
) to the end with the free -COO- group (the C terminus
![]() ).
).
![]() Shown below is the structure formed by three amino acids linked by peptide bonds. Select its name from the following list using the three-letter codes. Click on the Protein 1 icon to see the structures of the amino acids.
Shown below is the structure formed by three amino acids linked by peptide bonds. Select its name from the following list using the three-letter codes. Click on the Protein 1 icon to see the structures of the amino acids.
Protein Sequences (Primary Structure)